-
About Bona
-
Microtia
-
Abnormal Shape
-
Community
-
Online consultation
Microtia
the center of MicrotiaCorrection Method
How to correct microtia
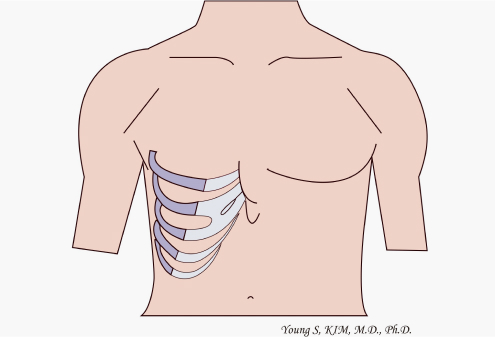
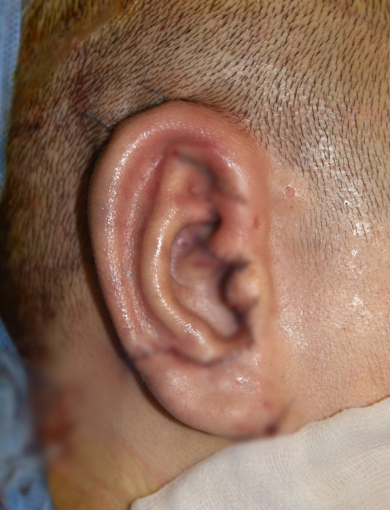
Microtia patients do not have a cartilage frame that can show the shape of their ears or the frame is incomplete, and the skin is absolutely lacking. So the following is needed in order to make a standing shape like the opposite normal
ear: 1) cartilage frame; 2) skin, and 1) chest cartilage, 2) alloplastic material(Medpor) as a cartilage frame.
Chest cartilage
As a representative surgical method for microtia, which began in earnest in 1959, chest cartilage is the most common method worldwide and has been verified for a long time.
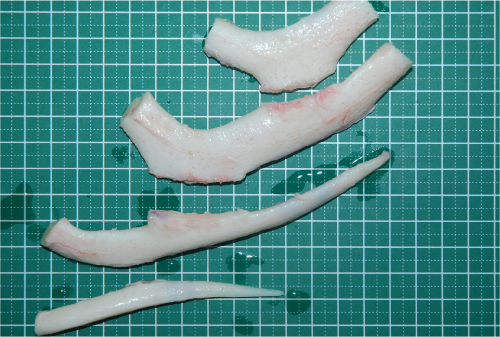
A large amount of cartilage is needed to make an ear cartilage frame, and cartilage in the chest area is the only place to get it.
Composed of cartilage at the beginning of the ribs, chest cartilage is hard as cartilage that is different from the cartilage in the ear.
With age, it becomes like bone due to calcification.
Usually, 3-4 pieces of cartilage are harvested to make a complex cartilage frame. In the case of children, those are harvested so that the cartilage can be created, preventing chest deformation that may occur after harvesting to some extent.
Right time for surgery
Since the sternum needs to grow to some extent, Asian children must be at least 10 years old to become candidates,
but we think that the 5th or 6th grade of elementary school is usually the right time.
Surgical method
Surgery is performed at 6-month intervals, with two surgeries the first and second.
01. First surgery
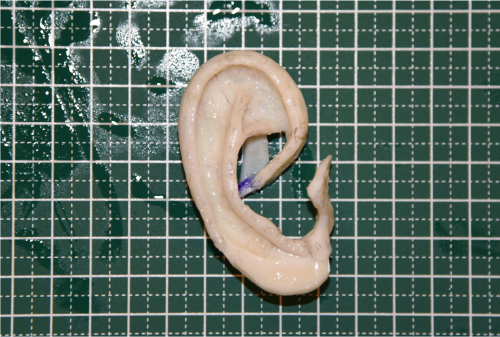
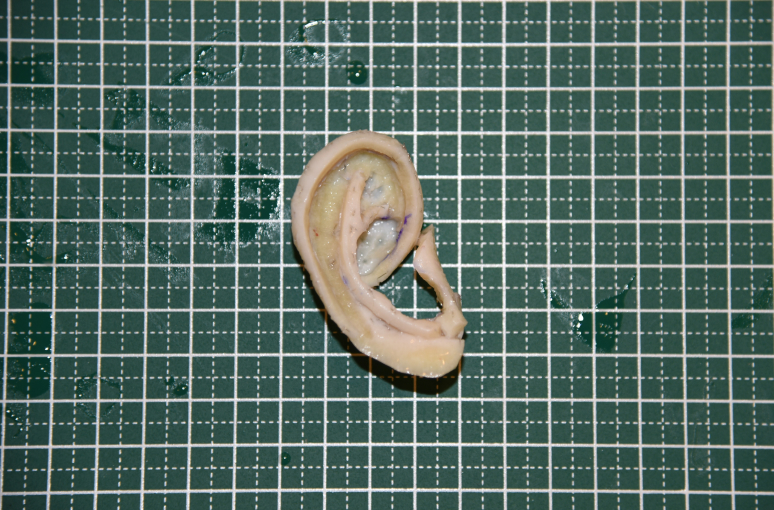
This is a process in which chest cartilage is harvested through an incision of about 4cm in the chest, an ear cartilage frame is made, and the skin behind the ear and the remaining microtia skin are used to cover.
The surgery is performed in two stages: the first to harvest the cartilage and prepare the ear transplant site (5-6 hours) and the second to implant the fabricated cartilage frame (2-3 hours).
All of them are performed in one day, and this method of performing two surgeries is adopted because it takes a considerable amount of time to elaborately make the ear cartilage frame, and the patient is lying on the operating table even under light anesthesia during this time, so recovery is slower later.
After the first, the patient moves to the ward and takes a rest (since intercostal anesthesia is applied to the area where the cartilage is harvested as the patient comes out, the pain is not severe while in the ward). An elaborate ear cartilage frame is made with the immediately harvested cartilage. After the cartilage production is complete, the patient moves back to the operating room for the surgery to implant the cartilage frame.
* Exceptionally, if there is a scar in front of the ear and the ear to be reconstructed is located in the hair (lower hairline), the ear is reconstructed as a standing ear from the beginning with flaps and fascia.
-
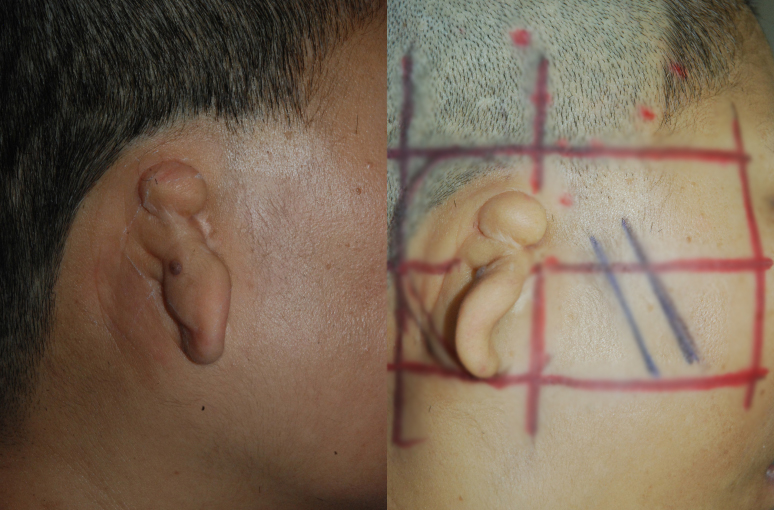
A 61-year-old patient who has undergone surgery for partial correction in the past,
has scars in the front and small ears, and has low hairline with hair at the position of
the ear to be reconstructed -
Right after surgery where reconstruction was performed with chest cartilage.
Reconstruction was performed as a standing ear from the beginning.
After 3-4 months, the remaining skin was simply removed with local anesthesia.
The picture on the right shows the appearance 1 year and 11 months after surgery.
02. Second surgery (7-8 hours)
This is the process of lifting the reconstructed ear attached to the
head to the same extent as the other side 6 months after the first surgery.
In the second surgery, in order to prevent complications such as
cartilage absorption that may occur over time and cover the support
that supports the ear cartilage frame, the fascia under the hair of the
temporal region, where blood circulation is very abundant, is used,
and the scalp skin is used to cover the area behind the ear.
Hospitalization and treatment after discharge
- Hospitalization
- First (general anesthesia):
Hospitalized the day before surgery, 3 nights 4 - Second (general anesthesia):
Hospitalized on the day of surgery, 2 nights and 3 days
- Treatment after discharge
- First: 3 weeks to 1 month of treatment required, dressing once every 2 days and 3 times a week
- Second: A month to 1 month and a half of treatment required, dressing once every 2 days and 3 times a week
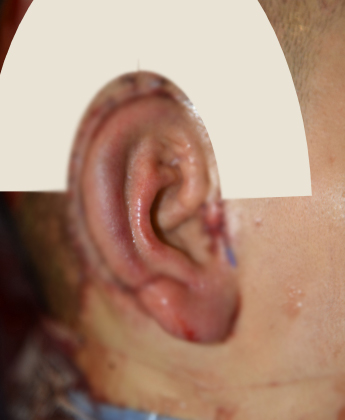
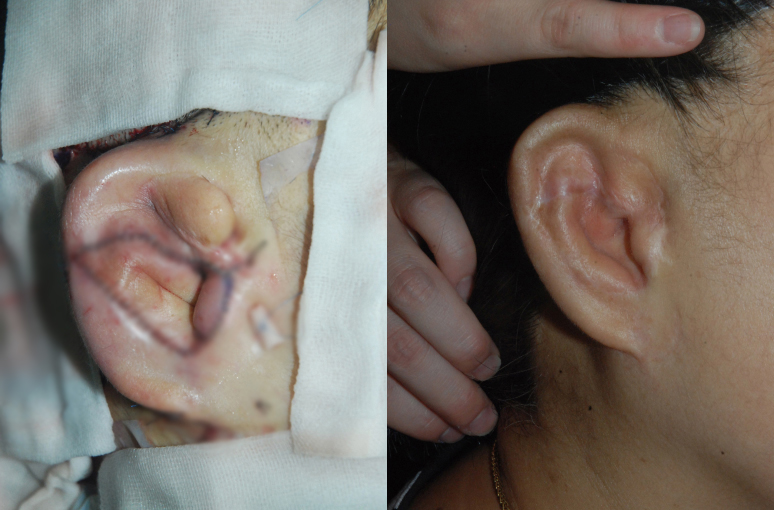
Appearance immediately
after second lifting surgery
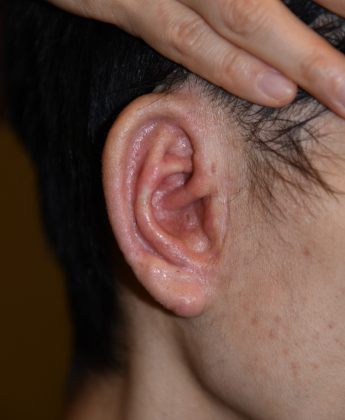
1 year and 8 months after first surgery,
1 year and 3 months after second lift
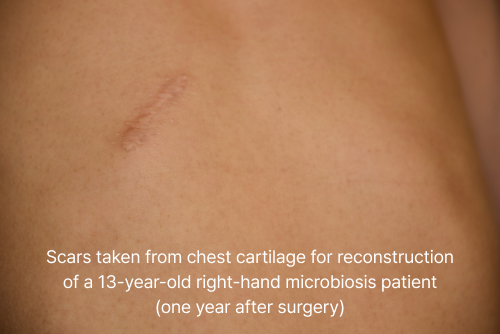
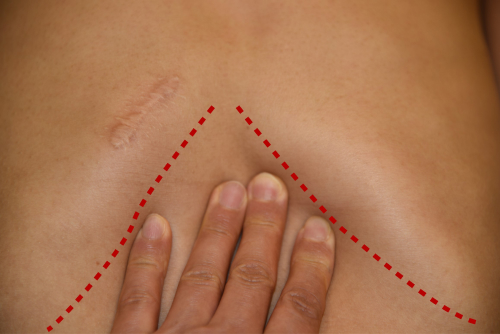
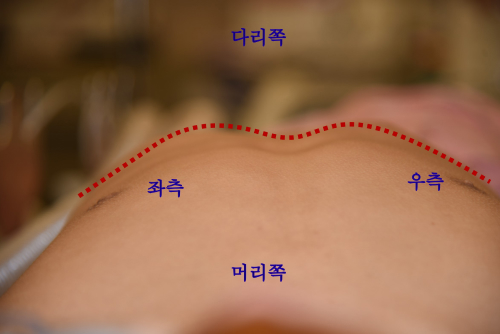
Chest scars and deformity
It shows that there is almost no deformation (chest depression) compared to the normal ribcage (left) even after cartilage is harvested. (1 year after chest cartilage collection)
The cases presented herein are intended to help understand microtia surgery, and are not the same for all patients, and the results may vary depending on various conditions such as the patient's constitution.
Complications after microtia surgery using chest cartilage
-
1Pneumothorax
(a phenomenon in which the lungs are filled with air due to damage to the pleura when cartilage is harvested) -
2Scalp scarring and hair loss
-
3Necrosis of cutaneous flap
-
4Exposure of transplanted chest cartilage
-
5Failure of skin graft
These complications may lead to additional surgery.
Other possible complications include facial nerve damage, infection, and exposure of the wire used to fix the cartilage.
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of chest cartilage and Medpor
-
Age & Surgery Method
Medpor Chest cartilage Age After age 5 After age 10, mostly 12-13 External auditory canal reconstruction External auditory canal reconstruction first After first surgery First surgery Reconstructed as a standing ear Transplanting a cartilage frame to the skin behind the ear Second surgery Removing the unnatural part after the first surgery Lifting the reconstructed ear -
Functional point of view
Medpor Chest cartilage Hearing recovery Possible early Possible after the first surgery Solidity Good to excellent (In the case of a frame pre-manufactured by Bona Clinic) Excellent for over 60 years Persistence Good to excellent No results over 30 years Proven for over 60 years -
Cosmetic point of view
Medpor Chest cartilage Extrusion and symmetry Advantageous for symmetry as it is reconstructed in a standing shape Asymmetry is likely to occur as it is transplanted under the skin behind the ear and lifted later Contours of the ear Relatively delicate auricle Slightly blunt auricle Skin graft Skin graft (American style) Skin graft required behind the ear after lifting Ear size Made based on the current ear size, and there may be a slight difference compared to normal ears. It can be made to a similar extent as it is made based on the ear that has almost grown -
Emotional aspect
Medpor Chest cartilage Emotional aspect Advantageous as the ear is reconstructed early Disadvantageous as it is performed usually after age 10 Number of surgeries 1-2 times 2 times Pain Almost no Chest pain usually lasts for about a week, but can be controlled with painkillers.
Case of Surgery
01. Classic Microtia
-
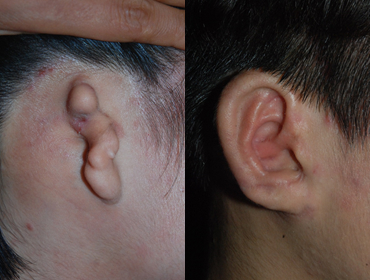 2 years and 3 months after surgery
2 years and 3 months after surgery -
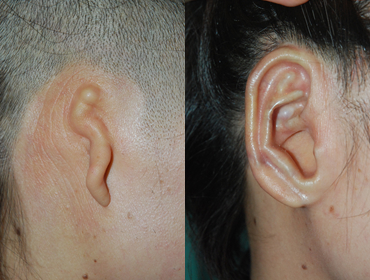 1 year and 7 months after surgery
1 year and 7 months after surgery -
Medpor
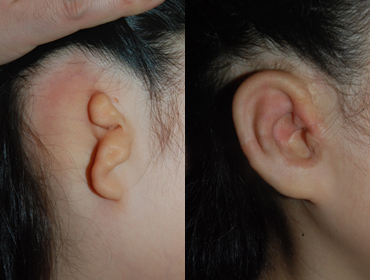 2 years after surgery
2 years after surgery -
Medpor
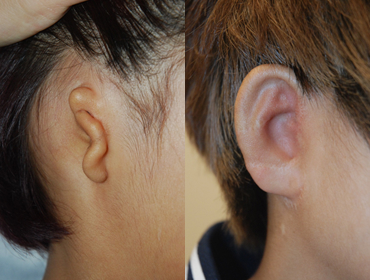 6 year and 2 months after surgery
6 year and 2 months after surgery
02. Small Atypical Microtia
-
Chest Cartilage
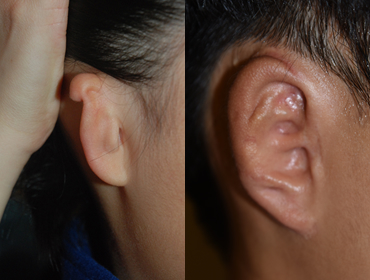 7 year and 7 months after surgery
7 year and 7 months after surgery -
Chest Cartilage
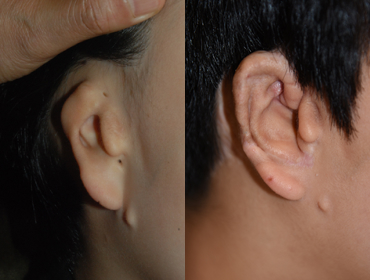 1 year and 9 months after surgery
1 year and 9 months after surgery -
Medpor
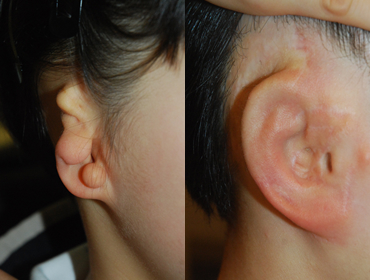 6 year and 10 months after surgery
6 year and 10 months after surgery -
Medpor
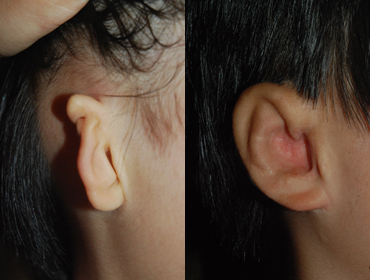 2 year and 6 months after surgery
2 year and 6 months after surgery
03. Atypical Microtia
-
Chest Cartilage
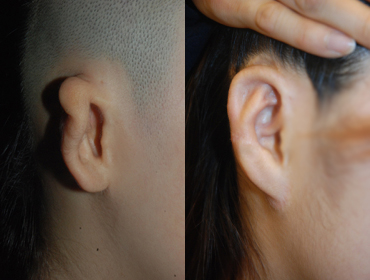 2 year and 6 months after surgery
2 year and 6 months after surgery -
Chest Cartilage
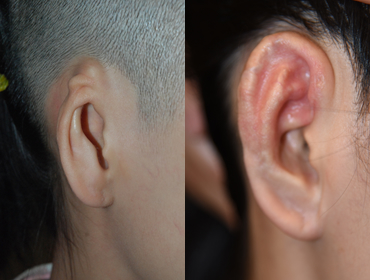 5 year and 2 months after surgery
5 year and 2 months after surgery -
Medpor
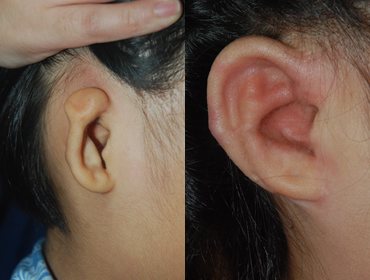 1 year and 2 months after surgery
1 year and 2 months after surgery -
Medpor
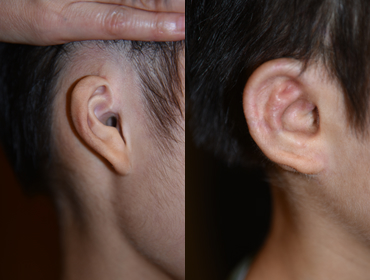 8 months after surgery
8 months after surgery
04. Microtia with low hairline
-
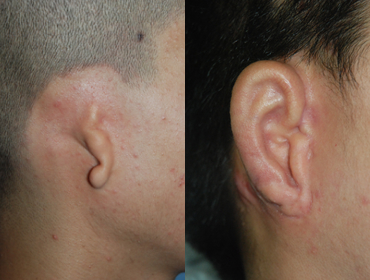 2 year and 1 months after surgery
2 year and 1 months after surgery -
 1 year and 3 months after surgery
1 year and 3 months after surgery
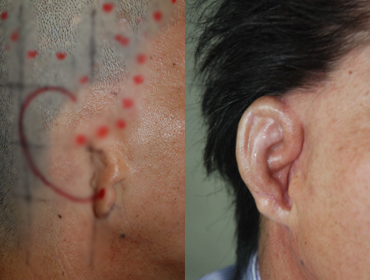
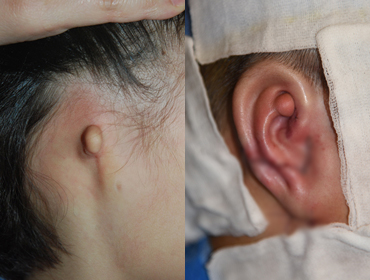
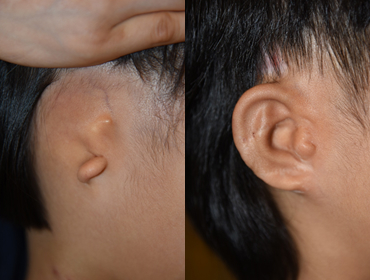
05. Aphasia
-
Chest Cartilage
 before surgeryimmediately after surgery
before surgeryimmediately after surgery -
Medpor
 1 year and 4 months after surgery
1 year and 4 months after surgery
Alloplastic material(Medpor)
Although chest cartilage is traditionally the most standardized method for microtia reconstruction, it has the disadvantages that it is necessary to wait until the upper grades of elementary school when the ribcage grows to a certain extent in order to harvest a large amount of cartilage, which should be harvested from one’s own chest.
From the past to the present, therefore, many studies on materials to replace chest cartilage have been conducted, but all of them ended in failure. However, after an attempt was made to use Medpor, which was originally used as a post-traumatic bone substitute, as an ear frame in 1993, ear reconstruction using Medpor was implemented in earnest in the United States, and it has been carried out in many countries since then. Originally, the name Medpor was the product name of the company that produced it for the first time, and it was made of “porous polyethylene”, and products with various names are being produced now. (Supor, Omnipore, etc.) Unlike chest cartilage, however, Medpor cannot be implanted under the skin. This is because it is a porous material, so when implanted under the skin, the skin and Medpor are strongly adhered, resulting in side effects that the skin becomes thinner over time and eventually exposed. In order to reduce these side effects, we use the method of harvesting the temporal fascia to cover and transplanting the skin on it. However, this type of skin graft is very unsatisfactory due to hypoesthesia and scars at the donor site as well as different texture and color of the transplanted skin.
So, at our hospital, these disadvantages are supplemented through reconstruction with a flap technique that uses the skin behind the ear and the remaining small ear as much as possible.
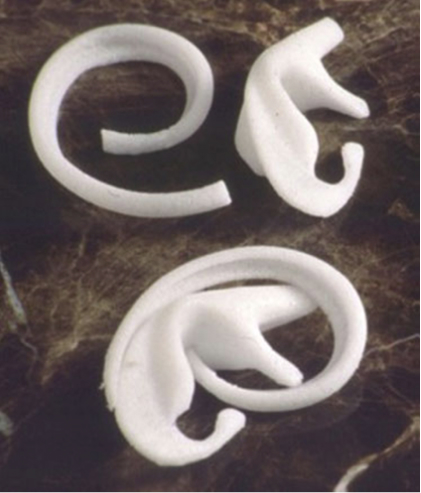

Medpor; The auricle and two bases are a pair,
and the cartilage frame is
made by combining these two.
Right time for surgery
The biggest advantage of Medpor is that surgery can be conducted early. If you think the emotional aspect of your child is important and want to do it before your child goes to school, the only way now is to use Medpor. Medpor surgery requires a certain period of treatment even after surgery, so it is recommended for those aged 5-6 because the child should be able to cooperate to some extent and must have awareness that he/she has undergone surgery in order to be careful even a little bit. Surgery using Medpor has the advantages of less pain and no scarring on the chest because no chest cartilage is harvested. However, Medpor can also have side effects, so you need to carefully consider various things before deciding on surgery.
Surgical method
In some cases, the surgery is conducted once, but the first and second surgeries are conducted at intervals of 4 to 6 months in most cases.
01. First surgery (general anesthesia, 7-8 hours)
-
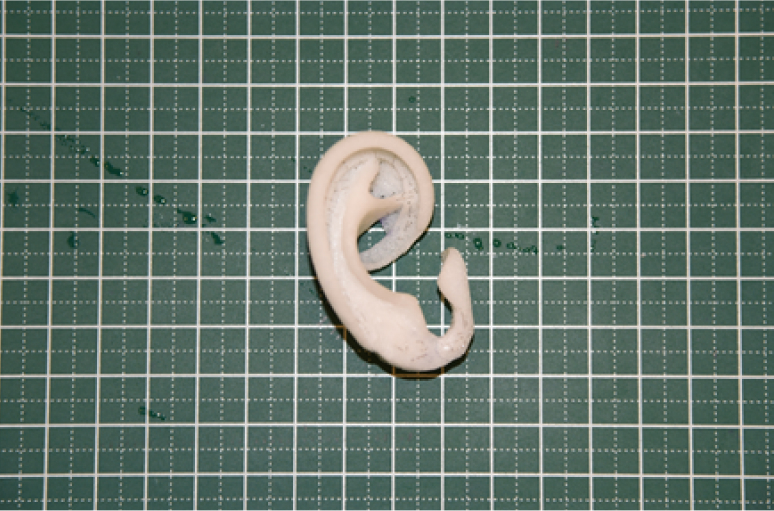

Fabricated Medpor ear cartilage frame
-
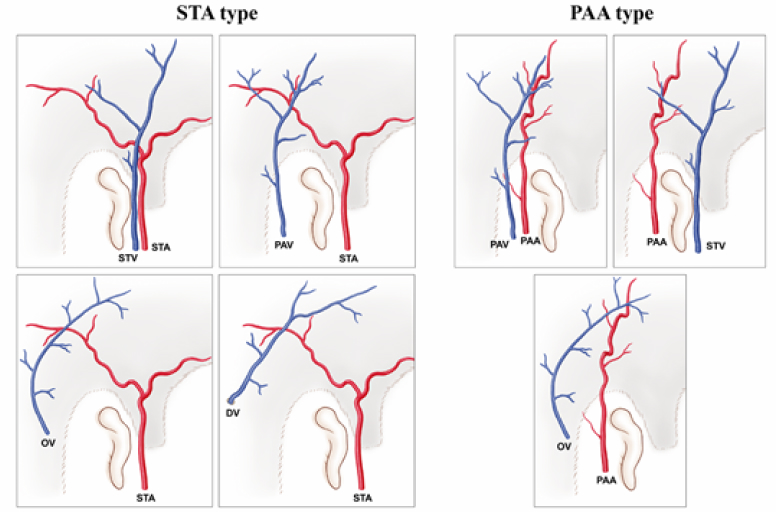
The main blood vessels supplied to the fascia are also distributed in various combinations.
-
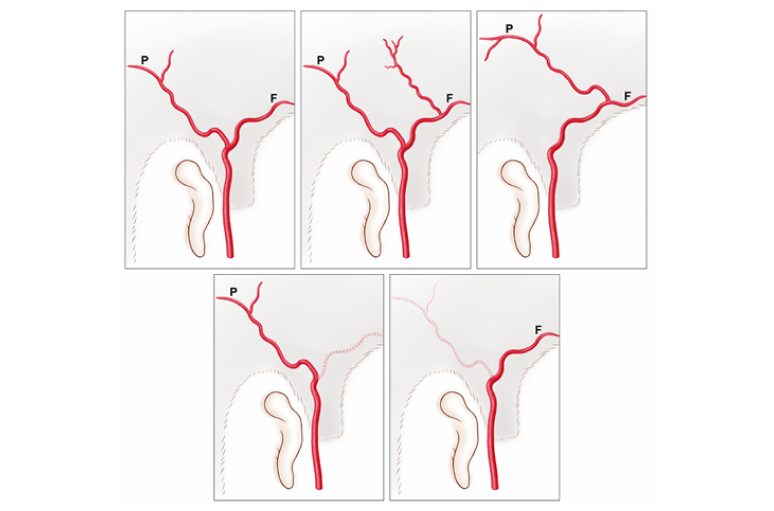
The temporal artery, known to most as the main artery
of the fascia, also presents in several forms.
Before the surgery, the process of elaborately refining the commercialized Medpor and making a stronger frame is performed for 2 to 2 hours and 30 minutes.
Unlike chest cartilage, Medpor should be made in a standing structure from the first time, so more skin is required. After general anesthesia, the flap behind the ear, the remaining small ear skin flap, and the scalp skin behind the ear are harvested and the fascia is lifted. The Medpor frame made is fixed to the exact position of the ear and covered with fascia and flaps.
The most important thing in surgery using Medpor is the temporal fascia, which must cover the frame of the part corresponding to the ear lobe and the part corresponding to the tragus without damaging the blood circulation. To do so, fascia of sufficient length and width must be harvested. Therefore, our hospital uses an incision method because the procedures using endoscopy performed in the United States are highly likely to vary in blood vessel travel and distribution, and have limitations in harvesting fascia with sufficient length and width due to thin blood vessels.
-
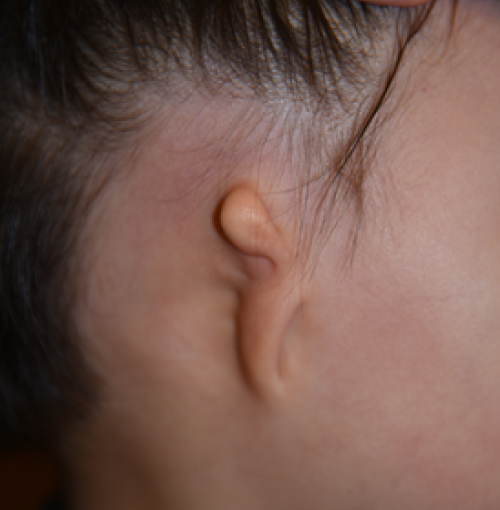
classic microtia
-
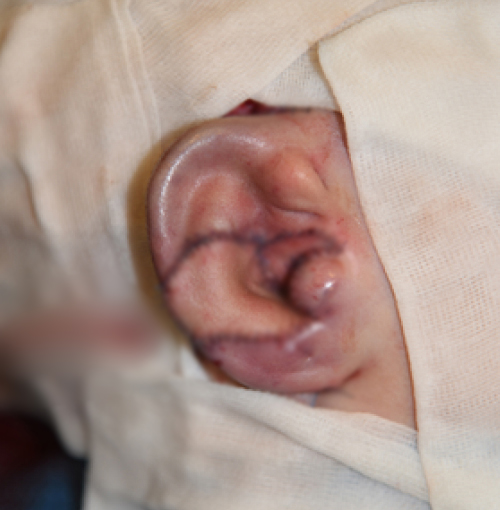
Immediately after surgery
-
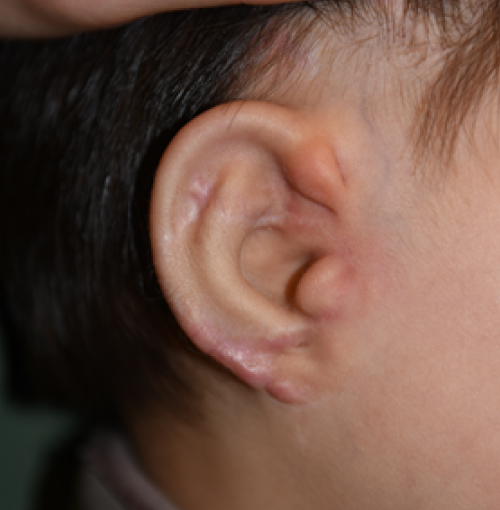
1 year and 1 month after first surgery
02. Second surgery (General anesthesia, 2-3 hours)
It is a relatively simple process to remove the remaining skin and other unnatural parts that were not removed during the first surgery 4-6 months after the first surgery.
Hospitalization and treatment after discharge
- Hospitalization
- First: Hospitalized on the day before surgery, 3 nights 4 days
- Second: Hospitalized on the day of surgery, discharge on the same day
- Treatment after discharge
- First: One month to one and a half months of treatment required, dressing once every 2 days and 3 times a week
- Second: Sutures are usually removed in 7 to 10 days, about 2 weeks of treatment required
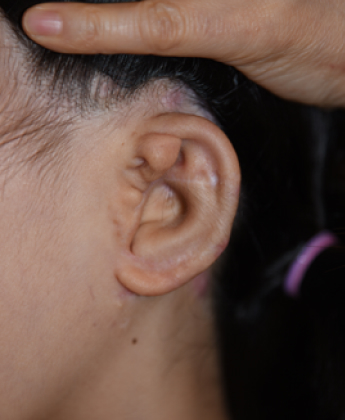
6 months and 27 days
after first surgery
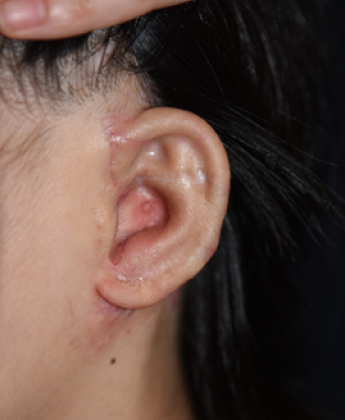
7 months and 13 days after
first surgery, 16 days after second surgery
Complications after Medpor surgery
-
1InflammationSince it is an artificial material, there is a risk of inflammation, but inflammation rarely occurs
-
2BreakageIf used in a commercialized form, it is highly likely to break in a weak area, but if a reinforced frame is made in the manner of our hospital, it rarely breaks.
-
3Skin congestion,
skin necrosisIf blood circulation in the skin flap is not smooth, congestion may occur, but congestion mostly gets better within two weeks due to fascia with smooth blood circulation underneath. In rare cases, necrosis can be easily resolved with skin transplantation. -
4Hair lossHair loss may occur in the scalp incision for fascia collection or the back of the ear for scalp skin collection. In the case of boys, it may be noticeable because their hair is short. Since children are young, the scalp scars are widened as they grow, and the hair loss is visible. In this case, after puberty, local anesthesia can be used to narrow the hair loss area to make it less noticeable. In most cases, hair grows in the area behind the ear where the skin was harvested.
-
5ExposureExposure is the main problem in surgery using Medpor. First of all, common cases are as follows: Not enough skin, facial paralysis, or hole surgery first, etc. You can see it occur even in normal cases. Therefore, if it is determined that exposure is likely to occur, surgery using chest cartilage is recommended afterwards, and efforts are made to lower the frequency with additional measures such as supplementing the thickness of the skin using artificial dermis etc. In addition, if side effects including exposure occur after a long period of time, it can be replaced with chest cartilage if you are of the right age.
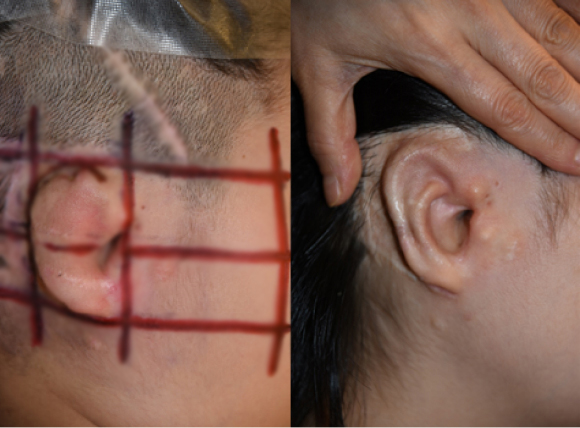
▶ This is a case in which medpore exposure occurred 8 years
and 5 months after surgery and was replaced with chest cartilage.
The complications listed above do not appear in all patients,
and additional surgery or treatment may be required when the above side effects occur.
In addition, the cases presented here are intended to help understand microtia surgery,
and the results may vary depending on various conditions such as the patient's constitution.
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of chest cartilage and Medpor
-
Age & Surgery Method
Medpor Chest cartilage Age After age 5 After age 10, mostly 12-13 External auditory canal reconstruction External auditory canal reconstruction first After first surgery First surgery Reconstructed as a standing ear Transplanting a cartilage frame to the skin behind the ear Second surgery Removing the unnatural part after the first surgery Lifting the reconstructed ear -
Functional point of view
Medpor Chest cartilage Hearing recovery Possible early Possible after the first surgery Solidity Good to excellent (In the case of a frame pre-manufactured by Bona Clinic) Excellent for over 60 years Persistence Good to excellent No results over 30 years Proven for over 60 years -
Cosmetic point of view
Medpor Chest cartilage Extrusion and symmetry Advantageous for symmetry as it is reconstructed in a standing shape Asymmetry is likely to occur as it is transplanted under the skin behind the ear and lifted later Contours of the ear Relatively delicate auricle Slightly blunt auricle Skin graft Skin graft (American style) Skin graft required behind the ear after lifting Ear size Made based on the current ear size, and there may be a slight difference compared to normal ears. It can be made to a similar extent as it is made based on the ear that has almost grown -
Emotional aspect
Medpor Chest cartilage Emotional aspect Advantageous as the ear is reconstructed early Disadvantageous as it is performed usually after age 10 Number of surgeries 1-2 times 2 times Pain Almost no Chest pain usually lasts for about a week, but can be controlled with painkillers.
Case of Surgery
01. Classic Microtia
-
 2 years and 3 months after surgery
2 years and 3 months after surgery -
 1 year and 7 months after surgery
1 year and 7 months after surgery -
Medpor
 2 years after surgery
2 years after surgery -
Medpor
 6 year and 2 months after surgery
6 year and 2 months after surgery
02. Small Atypical Microtia
-
Chest Cartilage
 7 year and 7 months after surgery
7 year and 7 months after surgery -
Chest Cartilage
 1 year and 9 months after surgery
1 year and 9 months after surgery -
Medpor
 6 year and 10 months after surgery
6 year and 10 months after surgery -
Medpor
 2 year and 6 months after surgery
2 year and 6 months after surgery
03. Atypical Microtia
-
Chest Cartilage
 2 year and 6 months after surgery
2 year and 6 months after surgery -
Chest Cartilage
 5 year and 2 months after surgery
5 year and 2 months after surgery -
Medpor
 1 year and 2 months after surgery
1 year and 2 months after surgery -
Medpor
 8 months after surgery
8 months after surgery
04. Microtia with low hairline
-
 2 year and 1 months after surgery
2 year and 1 months after surgery -
 1 year and 3 months after surgery
1 year and 3 months after surgery
05. Aphasia
-
Chest Cartilage
 before surgeryimmediately after surgery
before surgeryimmediately after surgery -
Medpor
 1 year and 4 months after surgery
1 year and 4 months after surgery
Secondary reconstruction for microtia
For revision surgery of patients who have already undergone surgery for microtia, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the current condition and determine how to improve it. In other words, it is necessary to consider various things such as the current shape, location, how the surgery was performed before, and the current condition of the skin around the ear and scars.
Right time for surgery
Secondary reconstruction can be conducted after at least 6 months since the first surgery, and there should be no current inflammation findings. If there are inflammation or other abnormal findings, revision surgery can be conducted after treatment.
Surgical method
Surgery can be divided into two surgical methods depending on whether the current ear skin can be used.
01. How to fabricate and transplant a new cartilage frame using skin tissue around the ear while keeping the current skin as much as possible: Two times of surgery, first and second, are conducted in accordance with general microtia surgery.
-
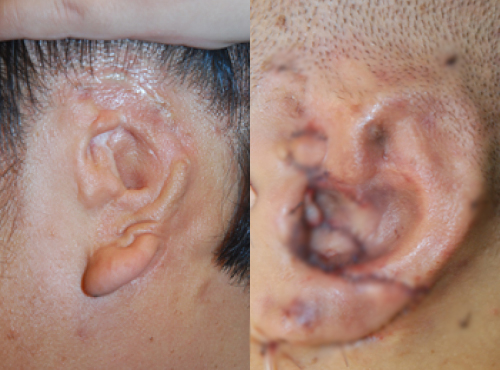
Left before surgery, right after surgery
-
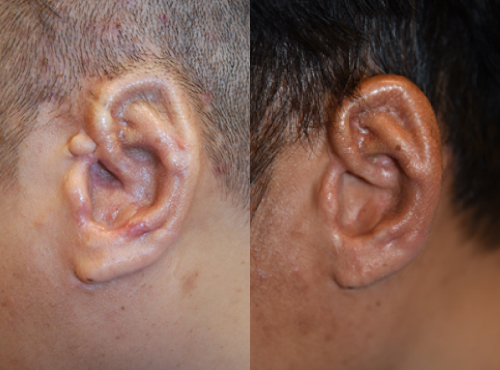
The left side is 6 months after primary surgery, the right side is 1 year and 7 months after primary surgery, and 1 year and 1 month after secondary surgery
-
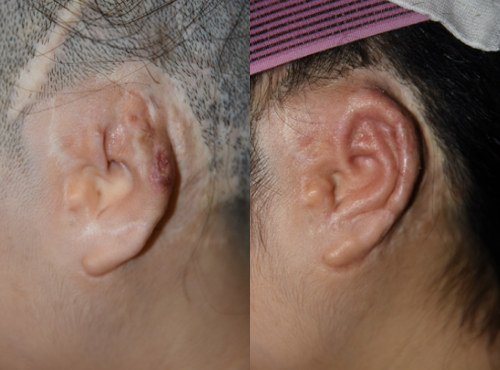
The left side was operated using medpore in the past, but there was repeated exposure and re-exposure occurred, and 8 years and 7 months have passed since the first surgery. On the right side, three months have passed after re-operation with the cartilage in the chest
02. Depending on the condition, it is done once or twice. Compared to using your own skin,
the texture and color of the skin may be different, so you may be less satisfied.
Depending on the condition, it is done once or twice.
Compared to using your own skin, the texture and color of the skin may be different,
so you may be less satisfied.
It is not a case of revision surgery, but it is a case where it is difficult to use
the skin behind the ear because there are scars in front and behind the ear due to
hole surgery in the past. In the case of revision surgery where the skin cannot be used,
reconstruction must be performed by grafting the fascia and skin as above.
Hospitalization and treatment after discharge
- Hospitalization
- First (general anesthesia):
Hospitalized the day before surgery, 3 nights 4 days - Second (general anesthesia):
Hospitalized on the day of surgery, 2 nights and 3 days
- Treatment after discharge
- First: 3 weeks to 1 month of treatment required, dressing once every 2 days and 3 times a week
- Second: A month to 1 month and a half of treatment required, dressing once every 2 days and 3 times a week
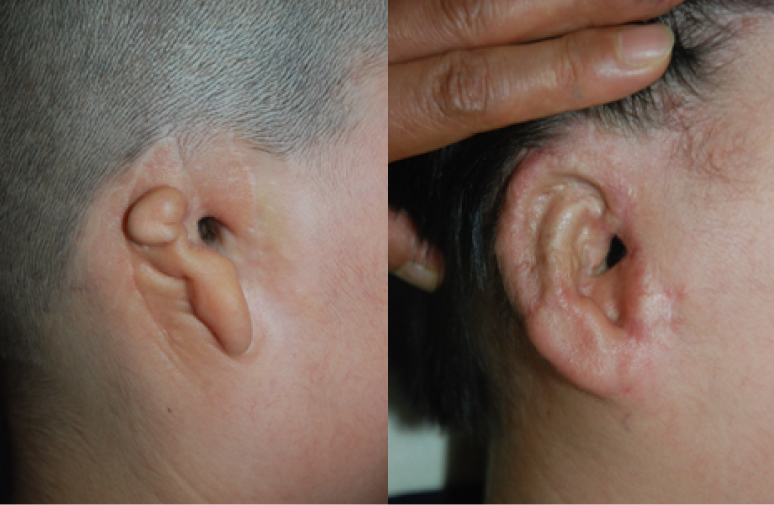
Consult with Bona Clinic.
information
-
Weekdays
10:00 ~ 19:00 Lunch time 13:00 ~ 14:00 -
Saturday
10:00 ~ 16:00 Lunch time 13:00 ~ 14:00 -
Directions
Line 3 Apgujeong
Station Exit 4 150m straight