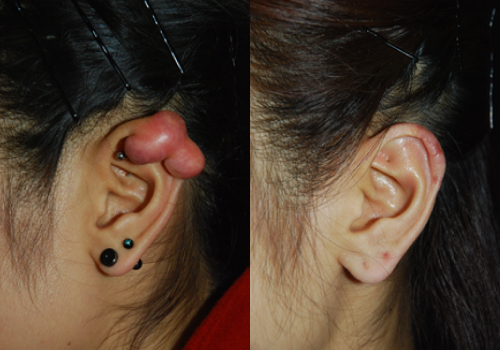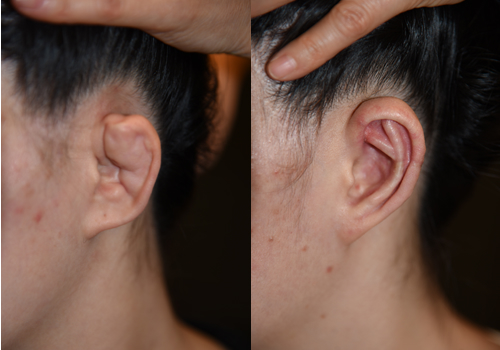Abnormal Shape
ear surgery centerOther deformities
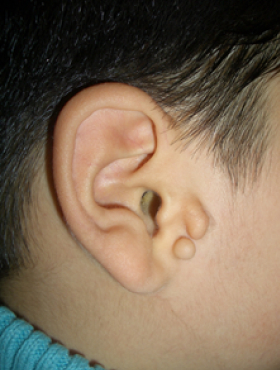
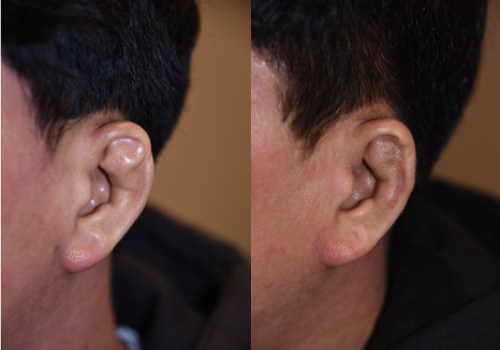
Tragal deformity
It is a form in which there are small protrusions of various shapes exist at the auricular part, most of which can be solved by simple excision, but sometimes there are complex deformities, so it is necessary to make it as natural as possible using the prominent part and surrounding tissue rather than simple excision.
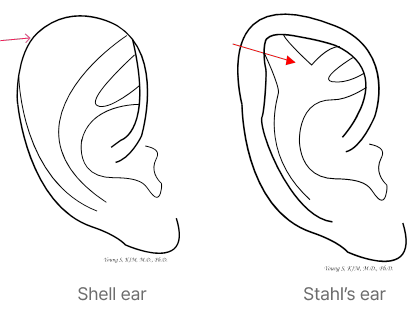
scaphoid ear, Shell ear,
Stahl’s ear
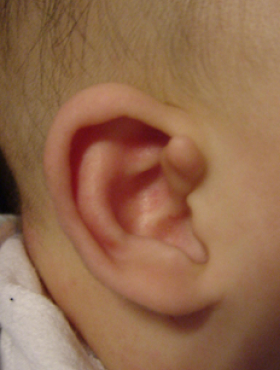
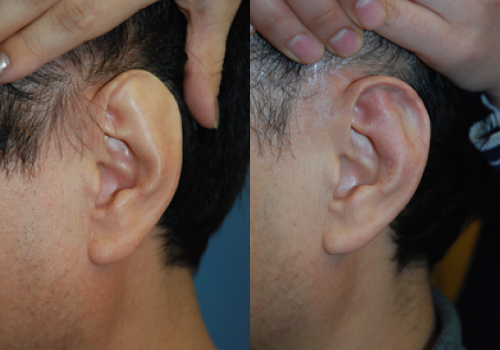
A scaphoid ear (shell ear) is a shape in which the thickness
of the helix is narrow or almost nonexistent
and the helix is flat in the shape of a shell.
In many cases,
it is merged with the prominent ear,
and it is necessary to
make the thickness of the helix
natural by using various methods.
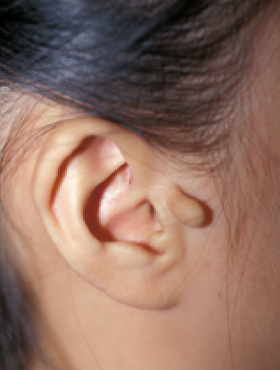
A Stahl’s ear is a thick pair of cartilage
between the rear upper
part of the antihelix and
the helix,
which is connected to each other
(called the third angle).
It is necessary to carefully shape the ear while removing this connection.
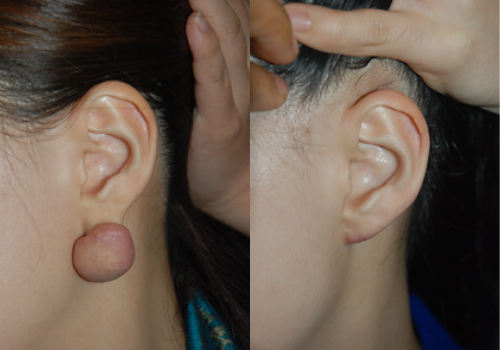
Keloid
A keloid is a deformation caused by excessive growth of abnormal fibrous tissue during the healing process of a wound. There is a constitutional factor, and it tends to occur in areas such as the chest and shoulders where there is generally no room for skin, but ears are also one of the most common areas. Keloids in the ear are most often caused by piercing. Due to continuous piercing even after wearing earrings and discharge from a wound, excessive fibrous tissue grows, causing itching and pain as well as cosmetic problems. Therefore, it is important to stop piercing and treat it early when there are symptoms of inflammation such as discharge at the beginning of the piercing. There are several treatments for keloids, such as injection therapy, pressure therapy, and radiation therapy, but it can be said that there is no definitive treatment. In most cases, simple injection therapy is attempted, but there are many cases of recurrence, and if the size is large, surgical treatment is eventually required, but the problem is recurrence. There is no way to say there is no recurrence yet, and it is best to reduce recurrence by using complex methods such as taking medicines that make scars less after surgery and pressure therapy. In particular, recurrent keloid correction should be carried out carefully, it is known that local radiation treatment after surgery minimizes recurrence. Above all, the most important thing in surgical correction of keloids in the ear is to preserve and restore the shape of the ear.
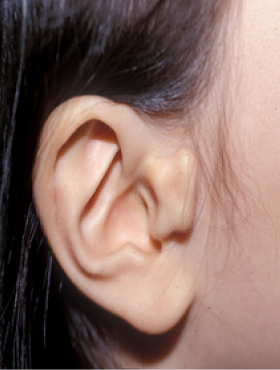
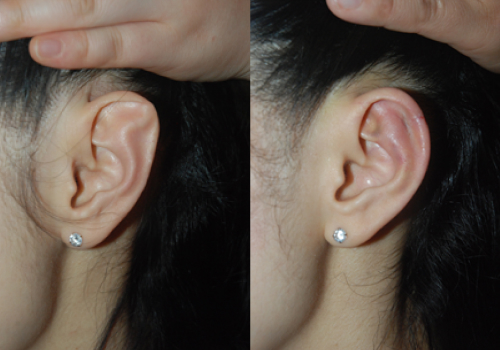
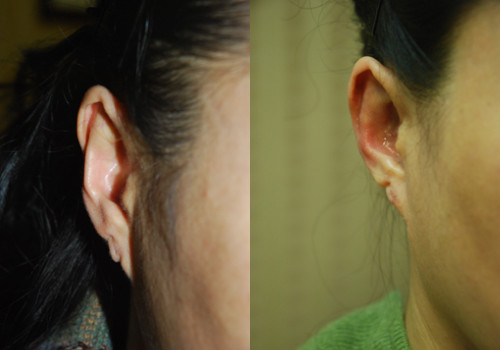
Contracted antihelix
Normally, the ears protrude about 2.0 cm away from the head, but there are cases where they are too attached to the head for congenital or acquired reasons (mostly caused by surgical treatment of the ear). Congenitally, due to the lack of the earflap, there is a case where the helix is not visible when viewed from the front, and the antihelix is relatively prominent, so it is expressed as lying down. For an acquired reason, most of them occur after surgical treatment, and it is common to see examples that are excessively attached to the head after prominent ear surgery.
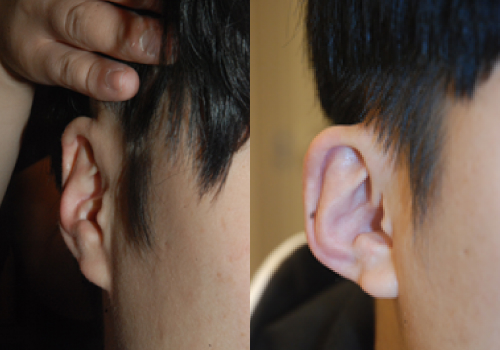
Dumpling ear (wrestler ear, cauliflower ear)
A cauliflower ear refers to a deformity that causes cartilage deformation as blood pools between the cartilage and the perichondrium due to continuous trauma and gradually hardens. We often see them in the ears of wrestlers or judo players, and they are called dumpling ears because they look like dumplings due to severe cartilage deformation. Depending on the severity, if mild, the dumpling ear can be corrected to some extent by excising the deformed cartilage part. In severe cases, however, a new cartilage frame must be made using chest cartilage to replace the original cartilage frame as in the surgical method for microtia. This is a mild dumpling ear and a case of correction by removing the cartilage.